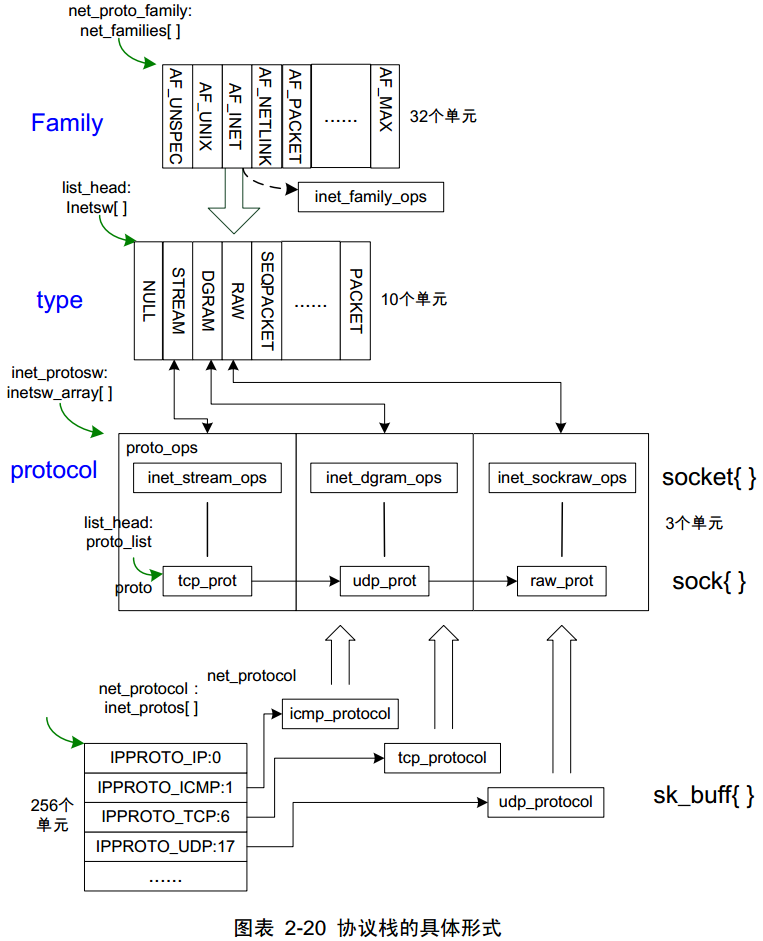
Linux网络协议栈初始化
Linux 网络协议栈初始化
(in developing)
-
- socket 和文件系统都位于 VFS 下一层,对 socket 的操作都要经过 VFS
-
- sock 初始化
- 2.1.
sock_init\(\) - 2.1. skb
- (skb 待补充)
- 2.2. sockfs 初始化
- 2.3. 网络过滤模块初始化
- 2.1.
- sock 初始化
-
- 网络协议初始化
- 3.1. 协议注册
proto_register\(\) - 3.2. 添加网络协议
inet_add_protocol\(\) - 3.3. 网络模块初始化
- 3.3.1.
dev_add_pack\(\)添加 packet 处理器
- 3.1. 协议注册
- 网络协议初始化
-
- 协议栈的其它初始化
-
- 总结
1. socket 和文件系统都位于 VFS 下一层,对 socket 的操作都要经过 VFS
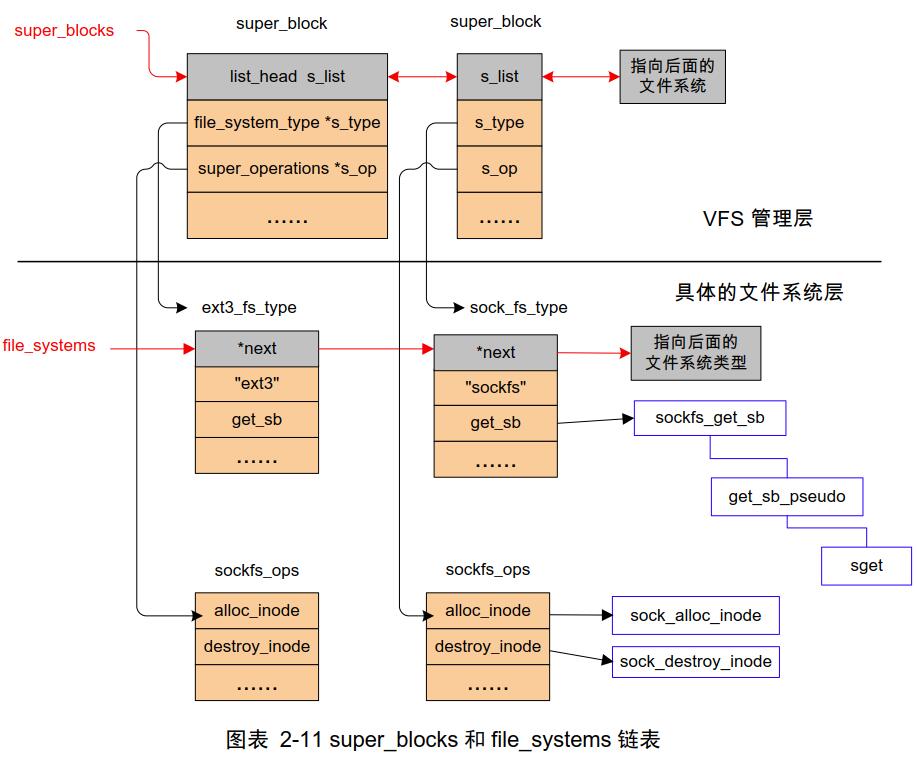
- linux 里面每个文件都有唯一的 inode ,inode 会大量使用,为了提高效率会对 inode 进行缓存;
- vfs 要调用具体的文件系统就需要知道每个文件系统的信息,这些信息都放在各自的超级块(super_block) 里,需要文件系统注册(
register_filesystem)把自己挂到 VFS 的file_systems全局链表上,然后通过挂载(kern_mount)自己、将超级块告知 VFS 。
2. sock 初始化
内核使用 init.h 中定义的初始化宏来进行,即将初始化函数放入特定的代码段去执行:
core_initcall(sock_init);
相关的宏和初始化函数还包括
core_initcall: sock_init
fs_initcall: inet_init
subsys_initcall: net_dev_init
device_initcall: 设备驱动初始化
上面四种宏声明的函数是按顺序执行的。
2.1. sock_init()
static int __init sock_init(void)
{
int err;
/*
* Initialize the network sysctl infrastructure.
*/
err = net_sysctl_init();
if (err)
goto out;
/*
* Initialize skbuff SLAB cache
*/
skb_init();
/*
* Initialize the protocols module.
*/
init_inodecache();
err = register_filesystem(&sock_fs_type);
if (err)
goto out_fs;
sock_mnt = kern_mount(&sock_fs_type);
if (IS_ERR(sock_mnt)) {
err = PTR_ERR(sock_mnt);
goto out_mount;
}
/* The real protocol initialization is performed in later initcalls.
*/
#ifdef CONFIG_NETFILTER
err = netfilter_init();
if (err)
goto out;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_NETWORK_PHY_TIMESTAMPING
skb_timestamping_init();
#endif
out:
return err;
out_mount:
unregister_filesystem(&sock_fs_type);
out_fs:
goto out;
}
sock_init() 可以分为 4 部分 : 初始化网络的系统调用(net_sysctl_init)、初始化 skb 缓存(skb_init)、初始化 VFS 相关(init_inodecache、 register_filesystem 、 kern_mount)、初始化网络过滤模块(netfilter_init)。
2.1. skb
数据包在应用层称为 data,在 TCP 层称为 segment,在 IP 层称为 packet,在数据链路层称为 frame。 Linux 内核中 sk_buff 结构来存放数据。
- sk_buff 结构体
struct sk_buff {
/* These two members must be first. */
struct sk_buff *next;
struct sk_buff *prev;
ktime_t tstamp;
struct sock *sk;
struct net_device *dev;
/*
* This is the control buffer. It is free to use for every
* layer. Please put your private variables there. If you
* want to keep them across layers you have to do a skb_clone()
* first. This is owned by whoever has the skb queued ATM.
*/
#ifdef CONFIG_AS_FASTPATH
char cb[96] __aligned(8);
#else
char cb[48] __aligned(8);
#endif
unsigned long _skb_refdst;
#ifdef CONFIG_XFRM
struct sec_path *sp;
#endif
unsigned int len,
data_len;
__u16 mac_len,
hdr_len;
union {
__wsum csum;
struct {
__u16 csum_start;
__u16 csum_offset;
};
};
__u32 priority;
kmemcheck_bitfield_begin(flags1);
__u8 local_df:1,
cloned:1,
ip_summed:2,
nohdr:1,
nfctinfo:3;
__u8 pkt_type:3,
fclone:2,
ipvs_property:1,
peeked:1,
nf_trace:1;
kmemcheck_bitfield_end(flags1);
__be16 protocol;
void (*destructor)(struct sk_buff *skb);
#if defined(CONFIG_NF_CONNTRACK) || defined(CONFIG_NF_CONNTRACK_MODULE)
struct nf_conntrack *nfct;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_BRIDGE_NETFILTER
struct nf_bridge_info *nf_bridge;
#endif
int skb_iif;
__u32 rxhash;
__be16 vlan_proto;
__u16 vlan_tci;
#ifdef CONFIG_NET_SCHED
__u16 tc_index; /* traffic control index */
#ifdef CONFIG_NET_CLS_ACT
__u16 tc_verd; /* traffic control verdict */
#endif
#endif
__u16 queue_mapping;
kmemcheck_bitfield_begin(flags2);
#ifdef CONFIG_IPV6_NDISC_NODETYPE
__u8 ndisc_nodetype:2;
#endif
__u8 pfmemalloc:1;
__u8 ooo_okay:1;
__u8 l4_rxhash:1;
__u8 wifi_acked_valid:1;
__u8 wifi_acked:1;
__u8 no_fcs:1;
__u8 head_frag:1;
/* Encapsulation protocol and NIC drivers should use
* this flag to indicate to each other if the skb contains
* encapsulated packet or not and maybe use the inner packet
* headers if needed
*/
__u8 encapsulation:1;
/* 6/8 bit hole (depending on ndisc_nodetype presence) */
kmemcheck_bitfield_end(flags2);
#if defined CONFIG_NET_DMA || defined CONFIG_NET_RX_BUSY_POLL
union {
unsigned int napi_id;
dma_cookie_t dma_cookie;
};
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_NETWORK_SECMARK
__u32 secmark;
#endif
union {
__u32 mark;
__u32 dropcount;
__u32 reserved_tailroom;
};
__be16 inner_protocol;
__u16 inner_transport_header;
__u16 inner_network_header;
#if defined(CONFIG_GIANFAR) && defined(CONFIG_AS_FASTPATH)
__u8 owner;
struct sk_buff *new_skb;
#endif
__u16 inner_mac_header;
__u16 transport_header;
__u16 network_header;
__u16 mac_header;
/* These elements must be at the end, see alloc_skb() for details. */
sk_buff_data_t tail;
sk_buff_data_t end;
unsigned char *head,
*data;
unsigned int truesize;
atomic_t users;
};
其中几个主要的成员是 :
struct sk_buff *next; //sk_buff 是以链表组织起来的,需要知道前后两个 sk_buff 的位置
struct sk_buff *prev;
struct net_device *dev; //数据报所属的网络设备
unsigned int len, //全部数据的长度
data_len; //当前 sk_buff 的分片数据长度
__be16 protocol; //所属报文的协议类型
__u8 pkt_type:3; //该数据包的类型
unsigned char *data; //保存的数据
atomic_t users; //每引用或“克隆”一次 sk_buff 的时候,都自加 1
协议类型
| 宏 | 值 | 说明 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ETH_P_802_2 | 4 | 真正的 802.2 LLC,当报文长度小于 1536 时 | |
| ETH_P_LOOP | 0x0060 | 以太网环回报文 | |
| ETH_P_IP | 0x0800 | IP 报文 | |
| ETH_P_ARP | 0x0806 | ARP 报文 | |
| BOND_ETH_P_LACPDU | 0x8809 | LACP 协议报文 | |
| ETH_P_8021Q | 0x8100 | VLAN 报文 | |
| ETH_P_MPLS_UC | 0x8847 | MPLS 单播报文 |
数据包类型
宏 |值 |说明 :– |:– |:– PACKET_HOST |0 |该报文的目的地是本机 PACKET_BROADCAST |1 |广播数据包,该 报文的目的地是所有主机 PACKET_MULTICAST |2 |组播数据包 PACKET_OTHERHOST |3 |到其他主机的数据包,在 VLAN 接口接收数据时有用 PACKET_OUTGOING |4 |它不是“发送到外部主机的报文”,而是指接收的类型,这 种类型用在 AF_PACKET 的套接字上,这是 Linux 的扩展 PACKET_LOOPBACK |5 |MC/BRD 的 loopback 帧(用户层不可见)
skb_init()
skb_init() 创建了两个缓存 skbuff_head_cache 和 skbuff_fclone_cache ,协议栈中所使用到的所有的 sk_buff 结构都是从这两个后备高速缓存中分配出来的,两者的区别在于前者是以 sizeof(struct sk_buff) 为单位创建的,是用来存放单纯的 sk_buff ,后者是以 2*sizeof(struct sk_buff)+sizeof(atomic_t) 为单位创建的,这一对 sk_buff 是克隆的,即它们指向同一个数据缓冲区,引用计数值是 0,1 或 2, 表示这一对
中有几个 sk_buff 已被使用。
- sk_buff 的使用
分配 alloc_skb()
销毁 kfree_skb()
分包/组包 :
(skb 待补充)
2.2. sockfs 初始化
网络通信可以被看作对文件的操作,socket 也是一种文件。网络初始化首先就要初始化 网络文件系统(sockfs)。
第一步是初始化 inode 缓冲(init_inodecache),为 sockfs 的 inode 分配一片高速缓存 :
static int init_inodecache(void)
{
sock_inode_cachep = kmem_cache_create("sock_inode_cache",
sizeof(struct socket_alloc),
0,
(SLAB_HWCACHE_ALIGN |
SLAB_RECLAIM_ACCOUNT |
SLAB_MEM_SPREAD),
init_once);
if (sock_inode_cachep == NULL)
return -ENOMEM;
return 0;
}
接着注册 sockfs 这种文件系统类型到 VFS 并将 sockfs 注册到 super_blocks :
...
init_inodecache();
err = register_filesystem(&sock_fs_type);
sock_mnt = kern_mount(&sock_fs_type);
...
这样以后创建 socket 就是在 sockfs 文件系统里创建一个特殊的文件,而文件系统的 super_block 里面有一个成员变量 struct super_operations *s_op; 记录了文件系统支持的操作函数,而这些操作函数都是让 VFS 来调用的,这样一来 socket 的表现就更像一个普通文件,支持大部分操作接口比如 write 、read 、close 等。
2.3. 网络过滤模块初始化
内核的 netfilter 模块详细内容可以参考 https://www.netfilter.org/。
网络过滤模块初始化函数 netfilter_init() 主要做了两件事:注册网 netfilter 络模块到每个网络 namespace 和初始化日志(本质也是注册日志模块到每个网络 namespace) 。
int __init netfilter_init(void)
{
...
ret = register_pernet_subsys(&netfilter_net_ops);
...
ret = netfilter_log_init();
...
}
3. 网络协议初始化
按照上文所述的协议栈初始化顺序, 网络文件系统初始化(sock_init) 结束之后就开始进入 网络协议栈初始化(由宏 fs_initcall 修饰的inet_init),这才开始真正的网络协议的初始化。
注意,网络协议的初始化是在网络设备的初始化之前完成的,在 Linux 系统中并不是说网络设备不 存在就不需要网络协议了,而是在没有网络设备存在的时候,照样可以完成网络的工作,只不过网络系 统物理上只存在于本机一台机器中而已。
static int __init inet_init(void)
{
...
sysctl_local_reserved_ports = kzalloc(65536 / 8, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!sysctl_local_reserved_ports)
goto out;
rc = proto_register(&tcp_prot, 1);
if (rc)
goto out_free_reserved_ports;
rc = proto_register(&udp_prot, 1);
if (rc)
goto out_unregister_tcp_proto;
rc = proto_register(&raw_prot, 1);
if (rc)
goto out_unregister_udp_proto;
rc = proto_register(&ping_prot, 1);
if (rc)
goto out_unregister_raw_proto;
(void)sock_register(&inet_family_ops);
...
/*
* Add all the base protocols.
*/
if (inet_add_protocol(&icmp_protocol, IPPROTO_ICMP) < 0)
pr_crit("%s: Cannot add ICMP protocol\n", __func__);
if (inet_add_protocol(&udp_protocol, IPPROTO_UDP) < 0)
pr_crit("%s: Cannot add UDP protocol\n", __func__);
if (inet_add_protocol(&tcp_protocol, IPPROTO_TCP) < 0)
pr_crit("%s: Cannot add TCP protocol\n", __func__);
#ifdef CONFIG_IP_MULTICAST
if (inet_add_protocol(&igmp_protocol, IPPROTO_IGMP) < 0)
pr_crit("%s: Cannot add IGMP protocol\n", __func__);
#endif
/* Register the socket-side information for inet_create. */
for (r = &inetsw[0]; r < &inetsw[SOCK_MAX]; ++r)
INIT_LIST_HEAD(r);
for (q = inetsw_array; q < &inetsw_array[INETSW_ARRAY_LEN]; ++q)
inet_register_protosw(q);
/*
* Set the ARP module up
*/
arp_init();
/*
* Set the IP module up
*/
ip_init();
tcp_v4_init();
/* Setup TCP slab cache for open requests. */
tcp_init();
/* Setup UDP memory threshold */
udp_init();
/* Add UDP-Lite (RFC 3828) */
udplite4_register();
ping_init();
/*
* Set the ICMP layer up
*/
if (icmp_init() < 0)
panic("Failed to create the ICMP control socket.\n");
/*
* Initialise the multicast router
*/
#if defined(CONFIG_IP_MROUTE)
if (ip_mr_init())
pr_crit("%s: Cannot init ipv4 mroute\n", __func__);
#endif
/*
* Initialise per-cpu ipv4 mibs
*/
if (init_ipv4_mibs())
pr_crit("%s: Cannot init ipv4 mibs\n", __func__);
ipv4_proc_init();
ipfrag_init();
dev_add_pack(&ip_packet_type);
rc = 0;
...
}
inet_init() 主要工作就是注册各种网络协议(如 icmp 、 tcp 、 udp 等)和初始化基础功能模块(如 arp 、 ip 等)。
网络协议初始化分两步: proto_register() 和 inet_add_protocol()。
3.1. 协议注册 proto_register()
kernel 定义了一个链表 proto_list ,所有的网络协议都要
挂到这个链表上,而 proto_register() 就是干这件事的。
每个网络协议在 kernel 内都是通过结构体 struct proto(net/sock.h) 表示的:
struct proto {
void (*close)(struct sock *sk,
long timeout);
int (*connect)(struct sock *sk,
struct sockaddr *uaddr,
int addr_len);
int (*disconnect)(struct sock sock*sk, int flags);
struct sock * (*accept)(struct sock *sk, int flags, int *err);
int (*ioctl)(struct sock *sk, int cmd,
unsigned long arg);
int (*init)(struct sock *sk);
void (*destroy)(struct sock *sk);
void (*shutdown)(struct sock *sk, int how);
int (*setsockopt)(struct sock *sk, int level,
int optname, char __user *optval,
unsigned int optlen);
int (*getsockopt)(struct sock *sk, int level,
int optname, char __user *optval,
int __user *option);
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
int (*compat_setsockopt)(struct sock *sk,
int level,
int optname, char __user *optval,
unsigned int optlen);
int (*compat_getsockopt)(struct sock *sk,
int level,
int optname, char __user *optval,
int __user *option);
int (*compat_ioctl)(struct sock *sk,
unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg);
#endif
int (*sendmsg)(struct sock *sk, struct msghdr *msg,
size_t len);
int (*recvmsg)(struct sock *sk, struct msghdr *msg,
size_t len, int noblock, int flags,
int *addr_len);
int (*sendpage)(struct sock *sk, struct page *page,
int offset, size_t size, int flags);
int (*bind)(struct sock *sk,
struct sockaddr *uaddr, int addr_len);
int (*backlog_rcv) (struct sock *sk,
struct sk_buff *skb);
void (*release_cb)(struct sock *sk);
/* Keeping track of sk's, looking them up, and port selection methods. */
void (*hash)(struct sock *sk);
void (*unhash)(struct sock *sk);
void (*rehash)(struct sock *sk);
int (*get_port)(struct sock *sk, unsigned short snum);
void (*clear_sk)(struct sock *sk, int size);
/* Keeping track of sockets in use */
#ifdef CONFIG_PROC_FS
unsigned int inuse_idx;
#endif
bool (*stream_memory_free)(const struct sock *sk);
/* Memory pressure */
void (*enter_memory_pressure)(struct sock *sk);
atomic_long_t *memory_allocated; /* Current allocated memory. */
struct percpu_counter *sockets_allocated; /* Current number of sockets. */
/*
* Pressure flag: try to collapse.
* Technical note: it is used by multiple contexts non atomically.
* All the __sk_mem_schedule() is of this nature: accounting
* is strict, actions are advisory and have some latency.
*/
int *memory_pressure;
long *sysctl_mem;
int *sysctl_wmem;
int *sysctl_rmem;
int max_header;
bool no_autobind;
struct kmem_cache *slab;
unsigned int obj_size;
int slab_flags;
struct percpu_counter *orphan_count;
struct request_sock_ops *rsk_prot;
struct timewait_sock_ops *twsk_prot;
union {
struct inet_hashinfo *hashinfo;
struct udp_table *udp_table;
struct raw_hashinfo *raw_hash;
} h;
struct module *owner;
char name[32];
struct list_head node;
#ifdef SOCK_REFCNT_DEBUG
atomic_t socks;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_MEMCG_KMEM
/*
* cgroup specific init/deinit functions. Called once for all
* protocols that implement it, from cgroups populate function.
* This function has to setup any files the protocol want to
* appear in the kmem cgroup filesystem.
*/
int (*init_cgroup)(struct mem_cgroup *memcg,
struct cgroup_subsys *ss);
void (*destroy_cgroup)(struct mem_cgroup *memcg);
struct cg_proto *(*proto_cgroup)(struct mem_cgroup *memcg);
#endif
};
接着调用 sock_register 添加一个 socket 的 handler , 而 inet_family_ops 的定义如下:
static const struct net_proto_family inet_family_ops = {
.family = PF_INET,
.create = inet_create,
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
};
表明自己的协议族(family)为 PF_INET,而成员函数 .create 是用来创建套接字的接口, 此处指定创建 PF_NET 套接字的接口函数就是 inet_create。
待补充结构体的详细解释
协议栈就定义了几个这样的结构体变量: tcp_prot 、 udp_prot 、raw_prot 、 ping_prot :
struct proto udp_prot = {
.name = "UDP",
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.close = udp_lib_close,
.connect = ip4_datagram_connect,
.disconnect = udp_disconnect,
.ioctl = udp_ioctl,
.destroy = udp_destroy_sock,
.setsockopt = udp_setsockopt,
.getsockopt = udp_getsockopt,
.sendmsg = udp_sendmsg,
.recvmsg = udp_recvmsg,
.sendpage = udp_sendpage,
.backlog_rcv = __udp_queue_rcv_skb,
.release_cb = ip4_datagram_release_cb,
.hash = udp_lib_hash,
.unhash = udp_lib_unhash,
.rehash = udp_v4_rehash,
.get_port = udp_v4_get_port,
.memory_allocated = &udp_memory_allocated,
.sysctl_mem = sysctl_udp_mem,
.sysctl_wmem = &sysctl_udp_wmem_min,
.sysctl_rmem = &sysctl_udp_rmem_min,
.obj_size = sizeof(struct udp_sock),
.slab_flags = SLAB_DESTROY_BY_RCU,
.h.udp_table = &udp_table,
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
.compat_setsockopt = compat_udp_setsockopt,
.compat_getsockopt = compat_udp_getsockopt,
#endif
.clear_sk = sk_prot_clear_portaddr_nulls,
};
struct proto tcp_prot = {
.name = "TCP",
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.close = tcp_close,
.connect = tcp_v4_connect,
.disconnect = tcp_disconnect,
.accept = inet_csk_accept,
.ioctl = tcp_ioctl,
.init = tcp_v4_init_sock,
.destroy = tcp_v4_destroy_sock,
.shutdown = tcp_shutdown,
.setsockopt = tcp_setsockopt,
.getsockopt = tcp_getsockopt,
.recvmsg = tcp_recvmsg,
.sendmsg = tcp_sendmsg,
.sendpage = tcp_sendpage,
.backlog_rcv = tcp_v4_do_rcv,
.release_cb = tcp_release_cb,
.hash = inet_hash,
.unhash = inet_unhash,
.get_port = inet_csk_get_port,
.enter_memory_pressure = tcp_enter_memory_pressure,
.stream_memory_free = tcp_stream_memory_free,
.sockets_allocated = &tcp_sockets_allocated,
.orphan_count = &tcp_orphan_count,
.memory_allocated = &tcp_memory_allocated,
.memory_pressure = &tcp_memory_pressure,
.sysctl_mem = sysctl_tcp_mem,
.sysctl_wmem = sysctl_tcp_wmem,
.sysctl_rmem = sysctl_tcp_rmem,
.max_header = MAX_TCP_HEADER,
.obj_size = sizeof(struct tcp_sock),
.slab_flags = SLAB_DESTROY_BY_RCU,
.twsk_prot = &tcp_timewait_sock_ops,
.rsk_prot = &tcp_request_sock_ops,
.h.hashinfo = &tcp_hashinfo,
.no_autobind = true,
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
.compat_setsockopt = compat_tcp_setsockopt,
.compat_getsockopt = compat_tcp_getsockopt,
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_MEMCG_KMEM
.init_cgroup = tcp_init_cgroup,
.destroy_cgroup = tcp_destroy_cgroup,
.proto_cgroup = tcp_proto_cgroup,
#endif
};
struct proto raw_prot = {
.name = "RAW",
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.close = raw_close,
.destroy = raw_destroy,
.connect = ip4_datagram_connect,
.disconnect = udp_disconnect,
.ioctl = raw_ioctl,
.init = raw_init,
.setsockopt = raw_setsockopt,
.getsockopt = raw_getsockopt,
.sendmsg = raw_sendmsg,
.recvmsg = raw_recvmsg,
.bind = raw_bind,
.backlog_rcv = raw_rcv_skb,
.release_cb = ip4_datagram_release_cb,
.hash = raw_hash_sk,
.unhash = raw_unhash_sk,
.obj_size = sizeof(struct raw_sock),
.h.raw_hash = &raw_v4_hashinfo,
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
.compat_setsockopt = compat_raw_setsockopt,
.compat_getsockopt = compat_raw_getsockopt,
.compat_ioctl = compat_raw_ioctl,
#endif
};
这几个对应的就是应用层的 stream 、 datagram 和 raw 等linux 的网络功能就要靠这几个协议支撑起来了。从结构体的成员变量可以看到我们平时使用
socket 要用到很多接口: getsockopt 、 connect 、 bind 等,当然这并不是
socket 直接使用的接口函数,肯定还要经过封装之后才能暴露给用户空间的。
proto_register() (net/core/sock.c) 的实现大致如下,就是讲协议变量挂到 proto_list 链表上,是连接传输层和网络层的纽带。
int proto_register(struct proto *prot, int alloc_slab)
{
..
mutex_lock(&proto_list_mutex);
list_add(&prot->node, &proto_list);
assign_proto_idx(prot);
mutex_unlock(&proto_list_mutex);
...
}
3.2. 添加网络协议 inet_add_protocol()
INET 是一种适合 Linux 的 TCP/IP 协议实现,它和用户层通信使用了 BSD Socket 接口。
inet_add_protocol() 的核心实现就一句话:
int inet_add_protocol(const struct net_protocol *prot, unsigned char protocol)
{
...
return !cmpxchg((const struct net_protocol **)&inet_protos[protocol],
NULL, prot) ? 0 : -1;
}
其中 cmpxchg 就是一个比较替换函数:比较第一个变量的值是否和第二个变量相等,相等的话则将第三个变量写入第一个变量。这里实际上就是检查 inet_protos[protocol] 所指向的内容是否为空,为空则表示该协议还没有添加,那么就可以把新协议添加到 inet_protos,完成添加协议,以后要用到某个协议就直接检索这个数组就行了,数组的定义如下:
const struct net_protocol __rcu *inet_protos[MAX_INET_PROTOS] __read_mostly;
其中 struct net_protocol 是专门给注册网络协议定义的结构体:
/* This is used to register protocols. */
struct net_protocol {
void (*early_demux)(struct sk_buff *skb);
int (*handler)(struct sk_buff *skb);
void (*err_handler)(struct sk_buff *skb, u32 info);
unsigned int no_policy:1,
netns_ok:1,
/* does the protocol do more stringent
* icmp tag validation than simple
* socket lookup?
*/
icmp_strict_tag_validation:1;
};
初始化协议栈时要添加的几种协议(igmp 、 tcp 、 udp 、 icmp)的 net_protocol 变量,其中成员变量 handler 负责处理收到的数据包,err_handler 负责错误处理,early_demux 待了解 :
#ifdef CONFIG_IP_MULTICAST
static const struct net_protocol igmp_protocol = {
.handler = igmp_rcv,
.netns_ok = 1,
};
#endif
static const struct net_protocol tcp_protocol = {
.early_demux = tcp_v4_early_demux,
.handler = tcp_v4_rcv,
.err_handler = tcp_v4_err,
.no_policy = 1,
.netns_ok = 1,
.icmp_strict_tag_validation = 1,
};
static const struct net_protocol udp_protocol = {
.early_demux = udp_v4_early_demux,
.handler = udp_rcv,
.err_handler = udp_err,
.no_policy = 1,
.netns_ok = 1,
};
static const struct net_protocol icmp_protocol = {
.handler = icmp_rcv,
.err_handler = icmp_err,
.no_policy = 1,
.netns_ok = 1,
};
Linux 区分永久和非永久协议。永久协议包括象 UDP 和 TCP,这是 TCP/IP 协议实现的基本部分,去 掉一个永久协议是不允许的。所以, UDP 和 TCP 是不能 unregistered。此机制由 2 个函数和一个维护注 册协议的数据结构组成。一个负责注册协议,另一个负责注销。每一个注册的协议都放在一个表里,叫 协议切换表。表中的每一个入口是一个 inet_protosw 的实例。
static struct inet_protosw inetsw_array[] =
{
{
.type = SOCK_STREAM,
.protocol = IPPROTO_TCP,
.prot = &tcp_prot,
.ops = &inet_stream_ops,
.flags = INET_PROTOSW_PERMANENT |
INET_PROTOSW_ICSK,
},
{
.type = SOCK_DGRAM,
.protocol = IPPROTO_UDP,
.prot = &udp_prot,
.ops = &inet_dgram_ops,
.flags = INET_PROTOSW_PERMANENT,
},
{
.type = SOCK_DGRAM,
.protocol = IPPROTO_ICMP,
.prot = &ping_prot,
.ops = &inet_dgram_ops,
.flags = INET_PROTOSW_REUSE,
},
{
.type = SOCK_RAW,
.protocol = IPPROTO_IP, /* wild card */
.prot = &raw_prot,
.ops = &inet_sockraw_ops,
.flags = INET_PROTOSW_REUSE,
}
};
在 inet_init() 中调用了多次 inet_register_protosw() 将 inetsw_array 数组注册到 inetsw ,分别对应 tcp 、 udp 、 icmp 、raw ,inetsw 会在以后创建 socket 时用到。
注意到结构体 inet_protosw 里面有一个成员变量 ops , 顾名思义指向的是和对应协议关联的操作函数,以 udp 的 ops 为例:
const struct proto_ops inet_dgram_ops = {
.family = PF_INET,
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.release = inet_release,
.bind = inet_bind,
.connect = inet_dgram_connect,
.socketpair = sock_no_socketpair,
.accept = sock_no_accept,
.getname = inet_getname,
.poll = udp_poll,
.ioctl = inet_ioctl,
.listen = sock_no_listen,
.shutdown = inet_shutdown,
.setsockopt = sock_common_setsockopt,
.getsockopt = sock_common_getsockopt,
.sendmsg = inet_sendmsg,
.recvmsg = inet_recvmsg,
.mmap = sock_no_mmap,
.sendpage = inet_sendpage,
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
.compat_setsockopt = compat_sock_common_setsockopt,
.compat_getsockopt = compat_sock_common_getsockopt,
.compat_ioctl = inet_compat_ioctl,
#endif
};
而 inet_dgram_ops 实际上和 udp_prot 是有关联的,最终 inet_dgram_ops 调用的函数都是 udp_prot 提供的。而 inet_dgram_ops 的成员函数是供 socket 使用的。
3.3. 网络模块初始化
如代码所述,网络模块初始化过程分为: ARP (arp_init())、 IP (ip_init(),这个函数又会调用 ip_rt_init 初始化路由表 )、 TCP Slab 缓存(tcp_init()) 、 UDP 存储(udp_init()) 、 UDP-lite (udplite4_register())、 ICMP 层(icmp_init()) 、 广播路由(ip_mr_init()) 、IPV4 mibs(Management Information Bases,管理信息库)(init_ipv4_mibs())、网络的 proc 文件系统(ipv4_proc_init()) 以及 IP 分包(ipfrag_init()),最后一个函数 dev_add_pack()。
3.3.1. dev_add_pack() 添加 packet 处理器
dev_add_pack() 的作用就是添加 packet 处理器,协议栈底层网络层有两种数据包: arp 和 ip,协议栈要区分处理。数据包类型抽象为结构体 packet_type :
struct packet_type {
__be16 type; /* This is really htons(ether_type). */
struct net_device *dev; /* NULL is wildcarded here */
int (*func) (struct sk_buff *,
struct net_device *,
struct packet_type *,
struct net_device *);
bool (*id_match)(struct packet_type *ptype,
struct sock *sk);
void *af_packet_priv;
struct list_head list;
};
而 ip 和 arp 都有自己的类型: ip_packet_type 、 arp_packet_type,前者在 inet_init 里直接通过通过 dev_add_pack() 注册,后者在 arp_init 里面使用 dev_add_pack() 注册,这样以后网络层收到数据包之后就先区分(id_match)再处理(func)。
具体流程待分析
4. 协议栈的其它初始化
core_initcall 阶段执行的初始化函数:
netpoll_initnet_inuse_init
fs_initcall 阶段执行的初始化函数:
init_sunrpcsun 开发的一种远程服务(RPC)服务eth_offload_initipv6_offload_initipv4_offload_initaf_unix_init本地 socket 初始化-
sysctl_core_init初始化 sysctlstatic __init int sysctl_core_init(void) { register_net_sysctl(&init_net, "net/core", net_core_table); return register_pernet_subsys(&sysctl_core_ops); }-
注册 sysctl 表(
net_core_table),net_core_table保存了系统运行过程中配置网络的所要使用到的/proc/net目录的参数和对应的实现函数等 :static struct ctl_table net_core_table[] = { #ifdef CONFIG_NET { .procname = "wmem_max", .data = &sysctl_wmem_max, .maxlen = sizeof(int), .mode = 0644, .proc_handler = proc_dointvec_minmax, .extra1 = &min_sndbuf, }, { .procname = "rmem_max", .data = &sysctl_rmem_max, .maxlen = sizeof(int), .mode = 0644, .proc_handler = proc_dointvec_minmax, .extra1 = &min_rcvbuf, }, { .procname = "wmem_default", .data = &sysctl_wmem_default, .maxlen = sizeof(int), .mode = 0644, .proc_handler = proc_dointvec_minmax, .extra1 = &min_sndbuf, }, { .procname = "rmem_default", .data = &sysctl_rmem_default, .maxlen = sizeof(int), .mode = 0644, .proc_handler = proc_dointvec_minmax, .extra1 = &min_rcvbuf, }, ...注册成功之后,系统运行过程中就可以通过修改
/proc/net下的文件来调整网络参数。 -
注册控制模块到每个网络 namespace
-
5. 总结
到此 Linux 网络协议栈的框架基本搭建起来了,初始化步骤基本结束。初始化过程可以简单分为几步:
- 初始化 sockfs 文件系统,因为 linux 下万物皆文件, socket 也不例外;
- 接着初始化网络的缓冲(
sk_buff),目的很明确就是利用 sk_buff 临时保存各种网络报文,提高网络效率; - 然后就是注册各种网络协议(tcp 、 udp 、 icmp 、 raw)和对应的操作接口;
- 最后就是初始化各种网络模块(arp 、 ip)、
/proc/net文件系统和各种网络服务。
linux 网络协议栈可以表示如下 :